Designing 21st century sustainable agriculture
It is not possible to conceive the world without food production and it is undeniable that agriculture and livestock are essential activities for the survival of the human being.
Sustainability: the Earth Overshoot day challenge
The concept of sustainable development emerged in the 1960s, when it became apparent that environmental problems could be caused by the development of the economy and industry. In 1972, the Club of Rome (NGO) presented its first report, known as the Meadows Report, at the first United Nations Conference on the Human Environment in Stockholm.
The report argued that non-growth in developing countries was a response to environmental deterioration and the scarcity of planetary resources, drawing particular attention to the “attack” on the capitalist system. For their part, economists claimed that capitalism could not survive without unlimited development, criticizing the report. Due to criticism, the Club of Rome issued a second report in 1974 advocating organic development, i.e. with limited growth intrinsic to all living organisms.
Since the publication of the book The Limits to Growth (Meadows et al., 1972), a considerable number of concepts were developed, integrating ecological and economic concerns that were not consensual until 1987. That year, the Brundtland Report was published, which defined “sustainable development” as one that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. Later, in 1997, Wackernagel and others popularized the term “ecological footprint” for the Earth Council. The authors determined the land needed to provide the natural resources consumed by the global population and the absorption of their waste. As a result, the term was adopted by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), which provides ecological footprint data from more than 150 nations listed in the Living Planet Report.
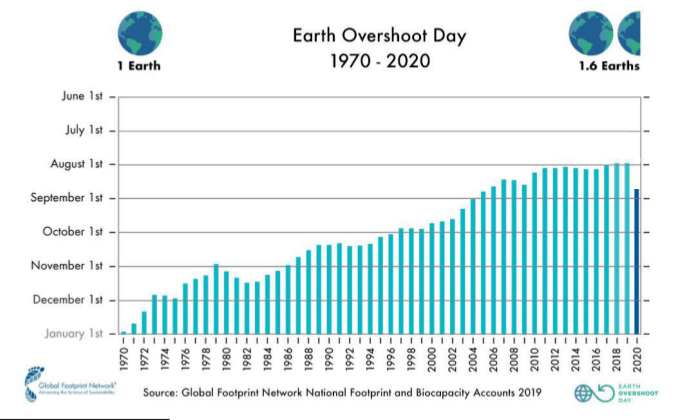
It is on the basis of this concept that the growing interest arises in quantifying the number of Earth planets we need to provide the resources needed for the use of humanity and to “absorb” emissions. Similarly, and because needs are already exceeding our planet’s capabilities, the concept of Earth Overshoot Day (EOD), the day of the year on which our planet’s capabilities are surpassed, has also been defined.
In 2019, the number of planets was already 1.75 and the EOD, or Earth Overload Day, was July 29, and action is urgently needed to address this global problem.
Feeding the world in today’s context
At the same time, agricultural, livestock and forestry systems have never faced such a wide range of complex challenges:
In addition, agricultural systems face the challenges posed by digital transformation. Decision-making technology and tools, based on new information and communication technologies related to precision agriculture, increasingly play an important role in addressing these challenges.
accelerating the digital transition in the agricultural sector will enable improved productivity as well as increased environmental performance, contributing to sustainable and efficient resource management.

ISQ operates throughout the value chain of the primary sector, providing integrated services and innovative technological solutions that allow to increase the competitiveness, sustainability and productivity of agro-industrial systems
ISQ’s role in this sector
Being a large Technological Interface Center, ISQ is a unique entity that brings together four complementary valences:
This allows ISQ not only to promote technology transfer and innovation in companies, through certification processes, improvement of quality and efficiency in production, support for innovation activities, access to technologies under development and training of human resources, but also to provide high quality and recognized services, in accordance with the most rigorous standards and applicable norms.
ISQ’s services for the agro-industry of the future, already today
Our regulatory and technological solutions and services for the agro-industrial sector contribute to achieving this vision and addressing the new challenges of a more global and competitive market.

QFA – the Unit for Chemistry, Pharmaceuticals and Agri-Food
ISQ has decided to combine the various valences it already has in the chemical, pharmaceutical and agri-food sectors with regard to analyses and trials, and has created a highly specialized unit called FFQ (Chemistry, Pharmaceutical and AgroAlimentar), dedicated to providing analysis services to various sectors of activity.
These are areas of activity with a high technological and scientific component, based on the accumulated experience of laboratory activity of the ISQ Group.
1) Soil, plant matter and water
Agricultural Analyses
The services provided by the Chemistry Laboratory of ISQ (LABQUI), cover a very wide range of tests ranging from Chemical Analyses to Environmental and Food Control.
Analytical services in the agricultural field have a strong impact on the safety of the sector, promoting not only the optimization of cultivation, fertilisation, harvesting and distribution processes as well as the promotion of safe agricultural production and protection of society in general through chemical and microbiological analysis of food.
The client enjoys a service of high professionalism, high quality standards, total exemption and impartiality in issuing results and technical opinions. You can also enjoy solutions tailored to your needs due to the laboratory’s capacity for innovation and entrepreneurship.
Labqui, in partnership with the Center for Operational and Irrigation Technologies (COTR), develops an integrated Agricultural Analysis service whose evaluation of the results gives rise to the issuance of recommendations / technical reports in order to meet the needs of plants, through a rigorous application of macro and micronutrients.
The recommendations/technical reports fall within the requirements of farmers’ field notebooks covered by certification standards such as Integrated Production, Organic Production, GLOBALGAP, BRC and Vulnerable Areas:
- Agricultural soils.
- Plant matter.
- Watering waters.
2) Food safety
Labiagro is a Chemical and Microbiological Laboratory of the ISQ group, dedicated to quality control and food safety. Endowed with a team of excellence with high training and experience and a unique laboratory structure, it has the most advanced technology and offers a set of differentiating services that are an integral and indispensable part for ensuring food safety and quality, contributing to a more conscious society.
Labiagro provides services to all food chain operators, including producers, industry, distributors, storers, from various sectors of activity. It provides knowledge as a complement in decision-making and presents specialized services and integrated solutions that result in a significant improvement in the performance levels of organizations involved in the food chain, improvement of their processes and consequently in safeguarding the health and well-being of consumers, thus contributing to the minimization of risks to public health.
The services are based on 3 main themes:
- Analytical Services: Chemical and Microbiological Analyses
- Consulting and Technical Support, Technical Solutions.
- Training
3) Transport and food contact packaging
Tests on packaging, materials, high consumption products and food contact
Through the National Packaging Center (CNE), ISQ Group Laboratory specialized in tests on packaging, materials, products of great consumption and food contact. The CNE develops tailored tests in several areas, in order to evaluate the performance of the products taking into account the purpose for which they are intended. Among the laboratory activity, we highlight the ability to evaluate materials and packaging through the following services:
- Evaluation of mechanical/physical properties, with tensile, compression, bending, among others.
- Climate tests: accelerated aging, temperature and humidity control, life cycle analyses.
- Product performance: leak assessment, integrity, impact, etc.
- Transport simulation, evaluation of packaging behavior: vibration, compression, falls, etc.
- Food contact, verification of compliance with European legislation, FDA, Council of Europe: global migration, specific migration, residual quantity, etc.
- Assessment of the suitability of the packaging to the product (protection, storage and distribution requirements).
- Optimization of packaging against your product.
- Evaluation and preparation of technical data sheets / declarations of conformity, and other supporting documents.
- Support services in the evaluation of documentation, tailored training actions, and conducting audits to suppliers.
4) Resources and waste

innovation in production fostering the circular economy
5) Systems and processes

promoting sustainability and productive efficiency
6) Safety and environment

ensure safety and environment
R&D+i and funding for 21st century agroindustry
ISQ is a percussor entity of technology and digitization in various sectors of the industry with extensive experience in national and international projects. In the R&D area related to agricultural systems, ISQ works on areas related to sustainability and resource efficiency in agriculture (water and energy) and animal farms, process digitization and digital decision support tools. The projects carried out include:
In addition to the R&D activity, ISQ also supports farmers and agro-industrialists in identifying funding opportunities in national and international programs.
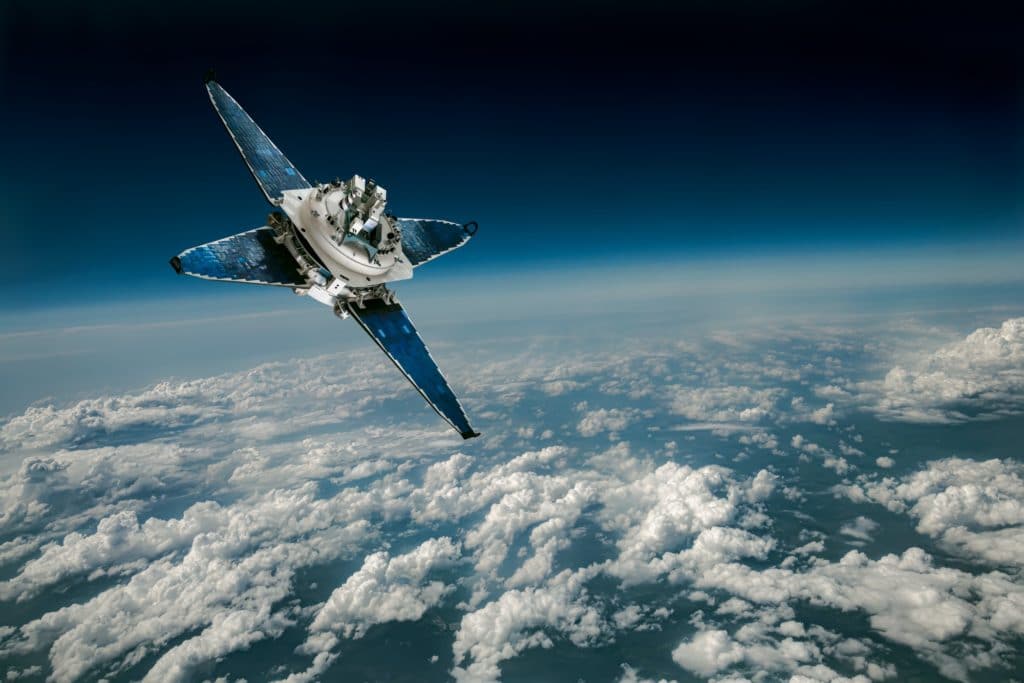

INTELICROP
Sustainable Agriculture through Earth Observation via Satellite and Data Science
The agricultural sector faces several challenges related to the increasing variability of climatic conditions, directly associated with the dynamics of crop growth, plant health, diseases and pest influxes.
InteliCROP (ESA SAMLL ARTES project) aims to provide technological decision support resources and services for sustainable agriculture, helping to develop preventive actions against phytosanitary problems or to improve crop management.
The solution developed by InteliCROP aims to improve the monitoring of agricultural variables, providing reliable information and forecasts on production, agricultural indicators, vegetation indices, or phytosanitary risks, with adequate advance notice to facilitate responses and contingency planning to better protect crops. .
The developed InteliCROP integrated platform leverages the capabilities of Earth observation methods and artificial intelligence methods to identify patterns and correlations in specific agro-climatic data for mapping occurrences in agriculture and promoting optimal decision-making.
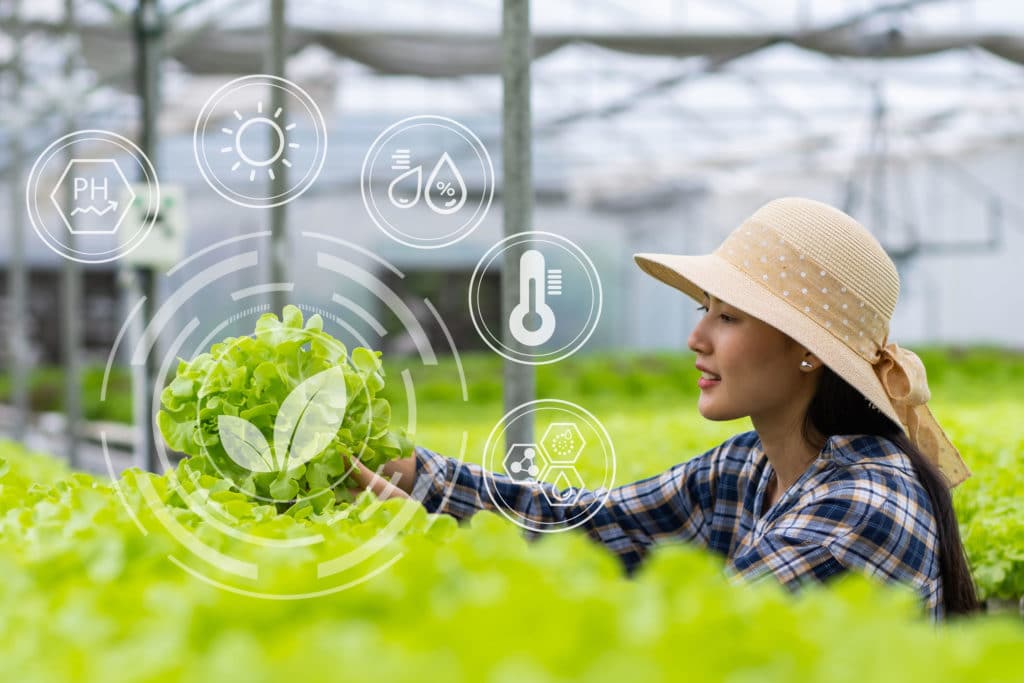

SMARTGREENHOUSE
Digital platform for greenhouse monitoring
As part of the MaisTec project, an IoT device was developed, a digital platform for monitoring greenhouses, SmartGreenHouse. The objective focuses on the contribution of sustainable agriculture by increasing knowledge of the culture media and intervening variables.
The IoT device allows you to measure in real time various indicators, eg temperature, air humidity, light, soil moisture (culture in substrate), electroconductivity of the irrigation solution (culture in hydroponics), pH of the irrigation solution (culture in hydroponics) , CO2, O2, air quality.
The measured data are sent wirelessly to a database integrated into the digital platform. The developed platform allows you to view the data history, monitor the measured variables in real time, or implement advanced models for data processing and analysis. Thus, the results are available in a web interface, with the possibility of also being presented in an android application.
related insights
more topics
Aeronautic/Aerospace (6) Agriculture and Agribusiness (1) Digital Transformation (2) Health and Life Sciences (3) Hydrogen (3) Industry 4.0 (3) Innovation (4) Renewable energy (6) Sustainability (12) Tourism (1)
+ insight
contribute
As a project initiated by ISQ, insight is open to contributions from everyone who wants to participate and who can bring their vision, scientific studies and reasoned opinion to enrich the themes and the debate.
If your activity is linked to research or the analysis and implementation of measures in the topics discussed here, please contact us using the form attached.





